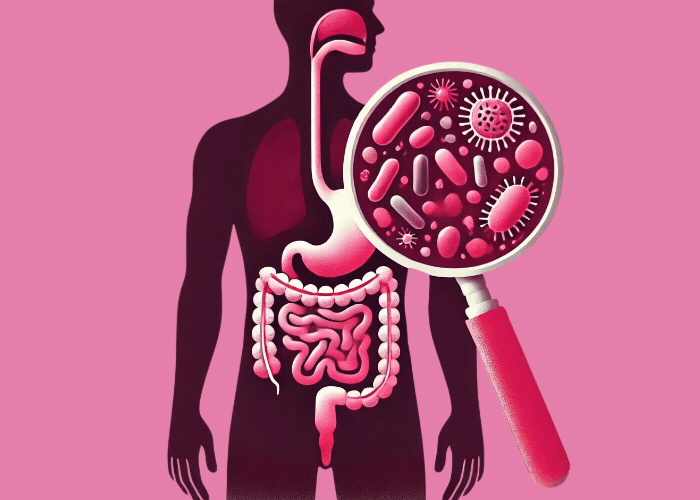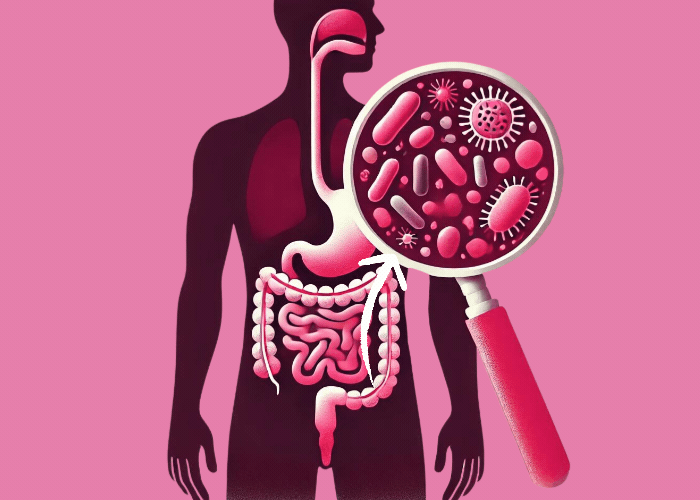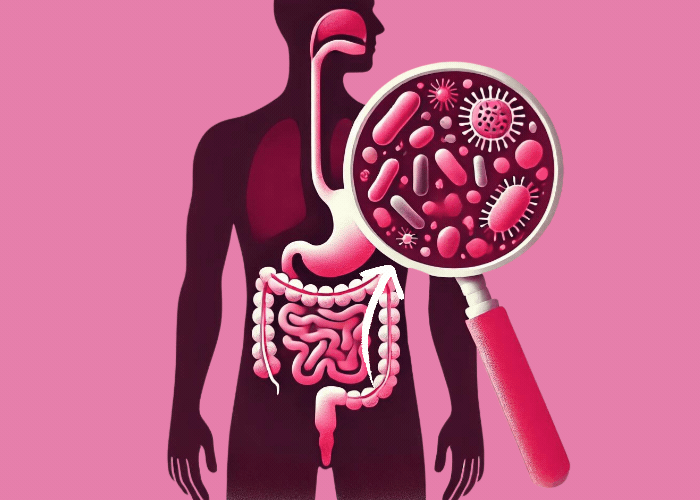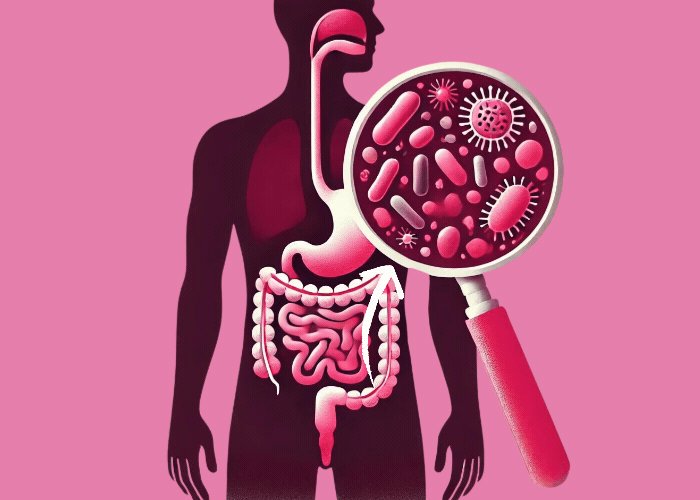
Probiotic bacteria play an important role in maintaining the intestinal barrier and can also positively influence the body’s own immune cells. They have also developed special mechanisms to deactivate unwanted intruders, like viruses, for example.
Protective mechanisms against viruses
The little helpers in our intestines use many of the following qualities to get the upper hand over the viruses that enter our bodies:

- Trapping mechanism: The term “trapping” is used quite literally. Certain bacterial strains can bind viruses to their cell surface and “trap” them there.
- Active release of antiviral substances: Certain bacterial strains can also produce so-called bacteriocins. These substances (e.g., hydrogen peroxide or lactate) can limit, among others, the propagation of viruses and interrupt the interaction of the virus with its target cell.
- Receptor blockade: There are many different receptors on the surface of cells (e.g., cells of the intestinal mucosa). Certain substances and viruses can then dock onto these receptors, and either cause a reaction within the cell or use it to directly enter the cell. What makes these receptors special is that they have very specific docking points: Not every substance can dock onto the receptor. Instead, both of the components need to fit together perfectly – like a key in a lock. Certain bacteria can also dock onto the surface of the cells in the intestinal mucosa – which prevents viruses from docking onto the same receptors and entering the cell.
- Macrophage activation: Probiotic bacteria can also activate so-called phagocytic cells (a.k.a. macrophages), that help clean the body from various harmful substances. Scavenger cells absorb the viruses and subsequently break them down.
The weapons that probiotic bacteria use against viruses
Bacteria are roughly 100 times bigger than viruses and can help our bodies fight them and protect us against diseases. Up next, we’ll explain the various mechanisms that we have at our disposal to protect us against viruses:
- Probiotic bacteria attach themselves to the surface of the virus and prevent them from infecting the cells in our body.
- Microorganisms produce substances that can destroy viruses.
- Probiotic bacteria block the docking points for viruses and prevent them from infecting the cells in our body.
- The layer of mucous in the intestines makes it difficult for viruses to move. This mucous also contains substances that deactivate the viruses.
- Probiotic bacteria stimulate the immune system and strengthen our defence system against viruses.